Data security is a practice that involves the protection of digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, destruction, modification, theft, or disclosure.
The process encompasses techniques and technologies such as the security of physical hardware (e.g., storage devices), logical security of software applications, administrative and access controls, organizational policy standards, and other data security practices.
On our exclusive Bootcamp with Thales and Forcepoint (March, 26th) we will learn about the importance of data protection, priorities, and predictions for 2024. Data Security Everywhere, an award-winning data security solution by the company Forcepoint ONE - Data Loss Prevention.
But firstly - Why is Data Security Important?
The core elements of data security include availability, confidentiality, and integrity. Below are some of the major reasons for implementing data security measures, especially for organizations that handle not only their data but also customer data:
- Compliance with industry and government regulations; it is critical to adhere to regulations for the business to carry on operating legally. The regulations exist to protect consumer privacy.
- Data security is also important because if a data breach occurs, an organization can be exposed to litigation, fines, and reputational damage to the company.
- Due to a lack of adequate data security practices, data breaches can occur and expose organizations to financial loss, a decrease in consumer confidence, and brand erosion. If consumers lose trust in an organization, they will likely move their business elsewhere and devalue the brand.
- Breaches that result in the loss of trade secrets and intellectual property can affect an organization’s ability to innovate and remain profitable.
Types of Data Security Technologies
There are various types of data security technologies in use today that protect against various external and internal threats. Organizations should be using many of them to secure all potential threat access points and safeguard their data. Below are some of the techniques:
Data encryption uses an algorithm to scramble every data character converting information to an unreadable format. Encryption keys from authorized users only are needed to decrypt the data before reading the files.
Encryption technology acts as the last line of defense in the event of a breach when confidential and sensitive data is concerned. It is crucial to ensure that the encryption keys are stored in a secure place where access is restricted. Data encryption can also include capabilities for security key management.
- Authentication
Authentication is a process of confirming or validating user login credentials to make sure they match the information stored in the database. User credentials include usernames, passwords, PINS, security tokens, swipe cards, biometrics, etc.
- Tokenization
Tokenization is similar to data encryption but differs in that it replaces data with random characters, whereas encryption scrambles data with an algorithm. The “token,” which relates to the original data, is stored separately in a database lookup table, where it is protected from unauthorized access.
- Data erasure
Data erasure occurs when data is no longer needed or active in the system. The erasure process uses software to delete data on a hardware storage device. The data is permanently deleted from the system and is irretrievable.
- Data resilience
Data resilience is determined by the ability of an organization to recover from incidences of a data breach, corruption, power failure, failure of hardware systems, or loss of data. Data centers with backup copies of data can easily get back on their feet after a disruptive event.
- Physical access controls
Unlike digital access control, which can be managed through authentication, physical access control is managed through control of access to physical areas or premises where data is physically stored, i.e., server rooms and data center locations. Physical access control uses security personnel, key cards, retina scans, thumbprint recognition, and other biometric authentication measures.
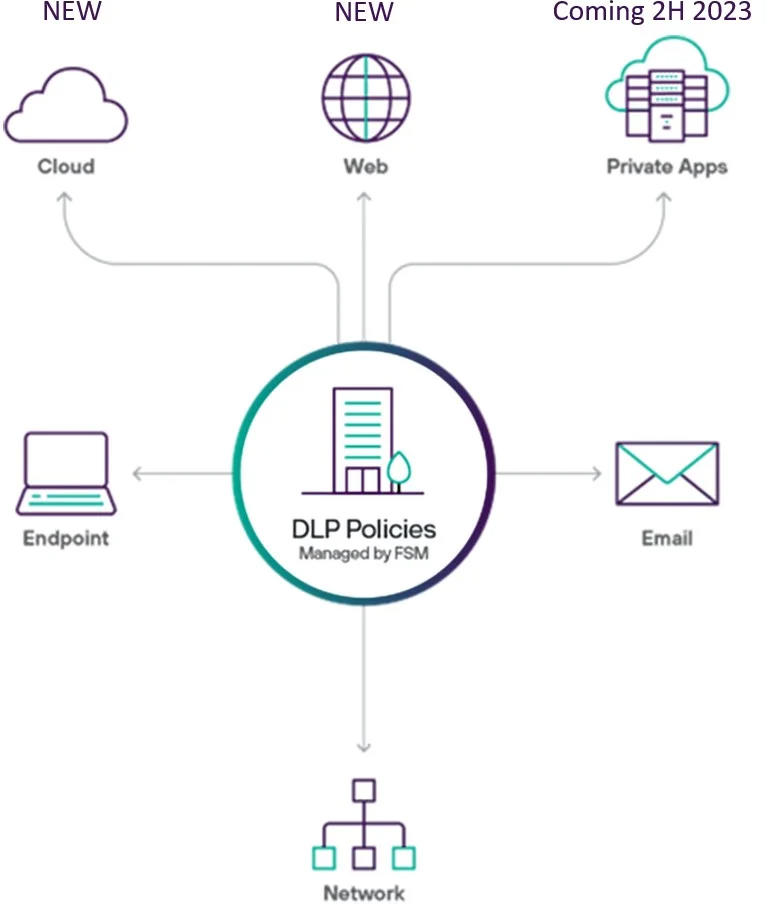
Forcepoint ONE DLP Solution
The Solution - Data Security Everywhere by Forcepoint
When it comes to deploying solutions, security professionals know that reaching time to value is more important than ever. This is especially true when selecting an SSE platform. When it comes to data security, organizations spend lots of people, time, and resources creating data policies to protect their organization's critical assets. Analysts tell us it can take even more time – as much as a year to completely replicate all of the policies when seeking to migrate policies to a new DLP.
Data Security Everywhere is an innovative approach that simplifies and unifies data security. Bring policy management and visibility to wherever your organization stores and uses data through a single, powerful data security solution. You can create one policy and deploy it everywhere by seamlessly combining industry-leading DLP solution with Forcepoint ONE SSE cloud platform.
A data security solution is only as good as the channels it protects. Contact an expert today about Data Security Everywhere or Bootcamp with Thales and Forcepoint 2024!